XSim version 2: simulation of modern breeding programs
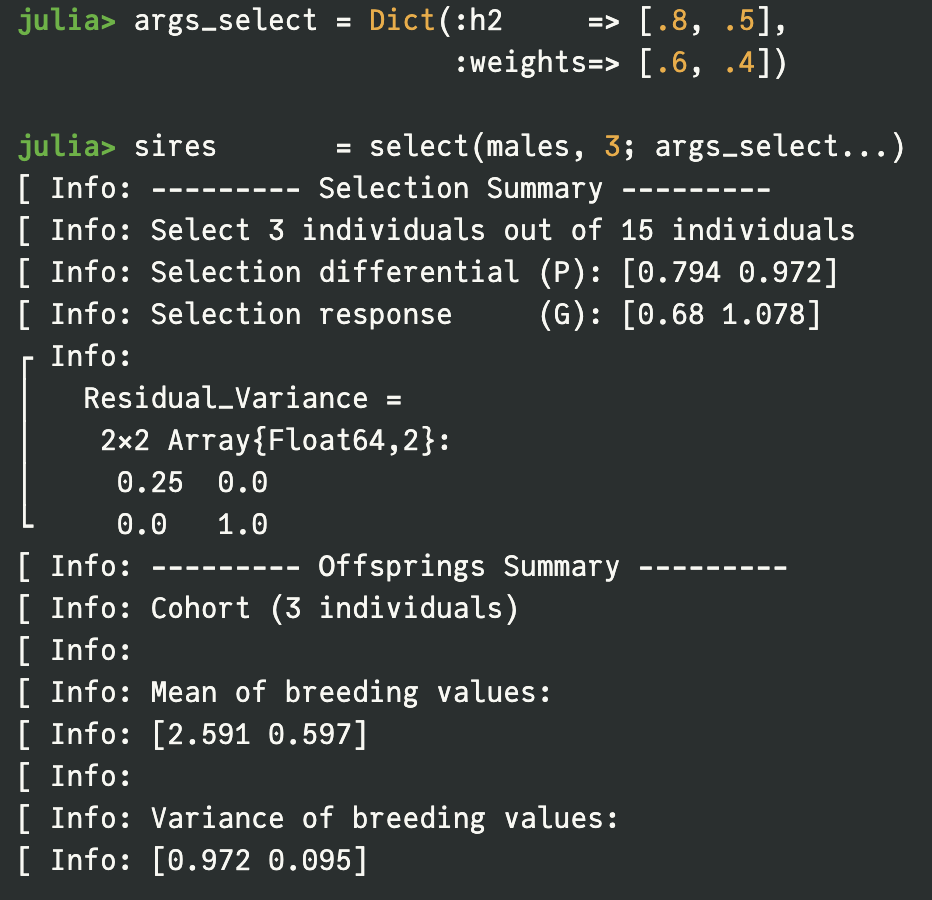
Streamlined Mating and Selection via Simple Syntax
XSimV2 simplifies the core breeding operations into two intuitive modular functions, mate() and select(), allowing users to concatenate, subset, and organize populations using straightforward operators like '+' or 'subset'. The library seamlessly integrates with the 'JWAS' package to perform genetic evaluations using advanced statistical models such as GBLUP and Bayesian Alphabets, enabling users to easily estimate breeding values (EBV) and simulate selection based on complex criteria like phenotypes or selection indices.
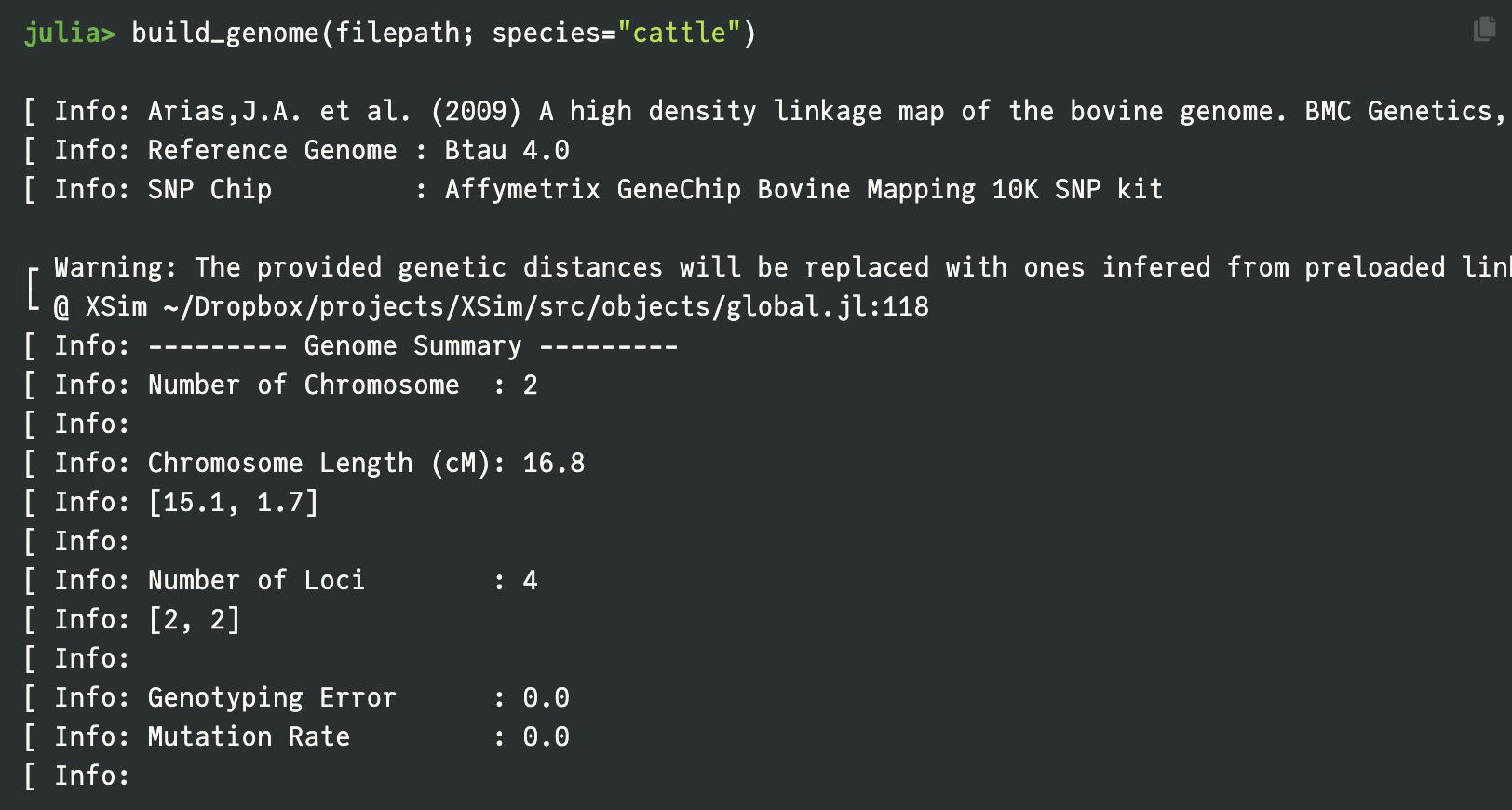
Realistic Genomic Simulations with Preloaded Reference Genomes
To facilitate immediate deployment, XSimV2 includes preloaded reference genomes from literature for major species like cattle, pigs, rice, and maize, allowing for the simulation of realistic recombination hotspots and cold spots without manual map construction. The tool employs an efficient 'drop-down' strategy that tracks chromosomal segment origins rather than every allele state, enabling the simulation of tens of thousands of individuals with sequence-level resolution while significantly reducing memory usage and computing time.
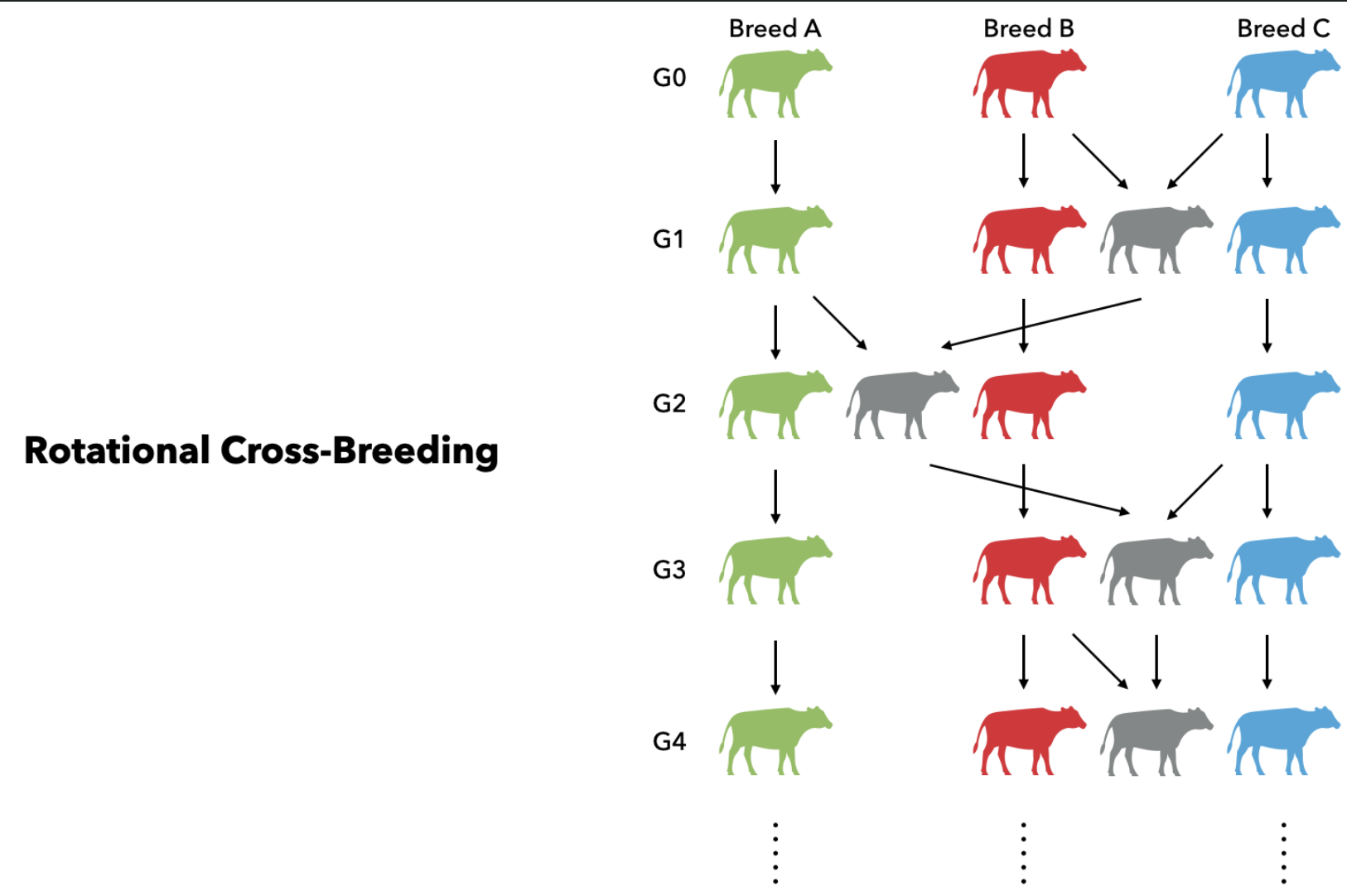
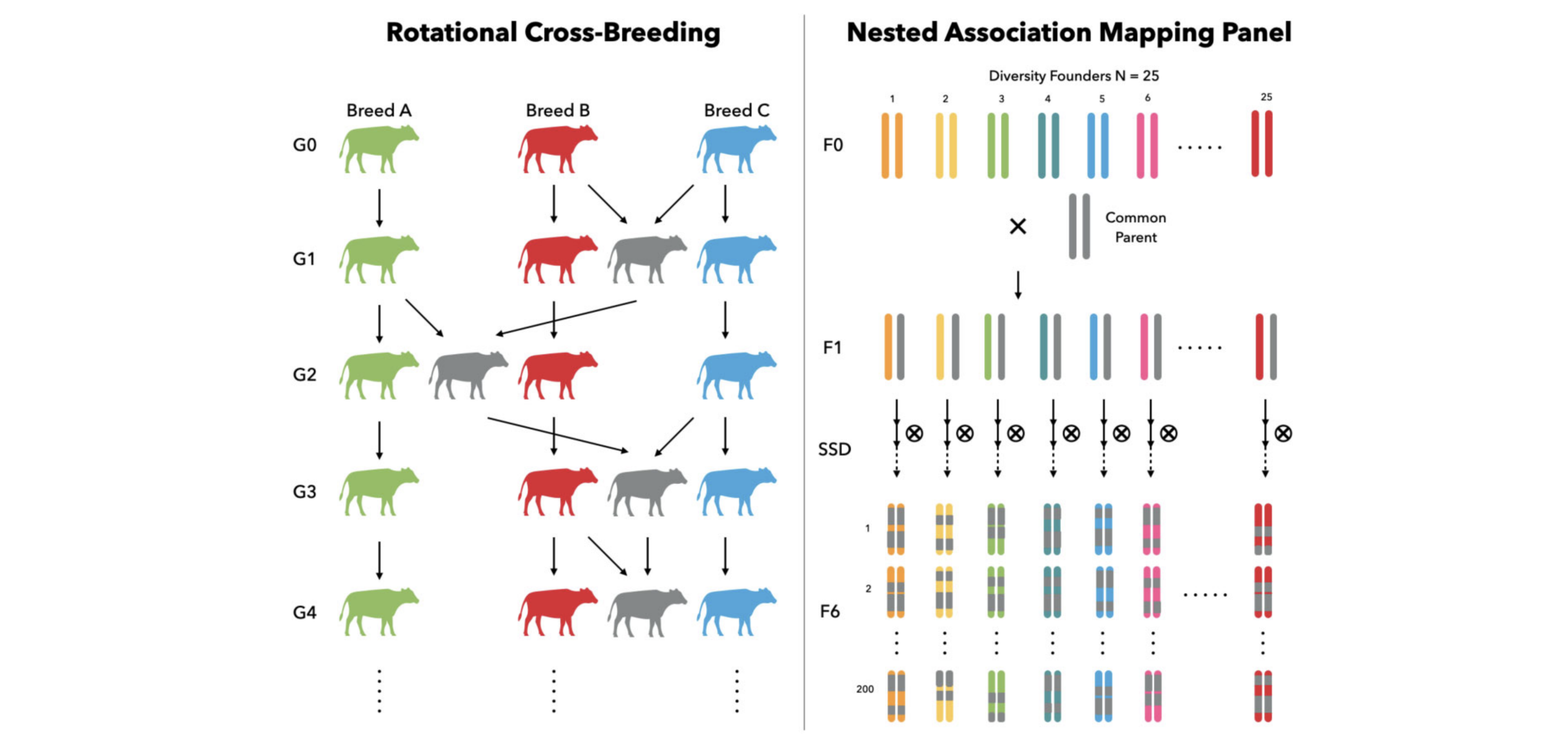
Flexible Adaptation to Complex Breeding Designs
The software's modular design allows researchers to effortlessly mimic intricate modern breeding programs, including rotational cross-breeding systems in cattle and multiparent Nested Association Mapping (NAM) designs in plants.
