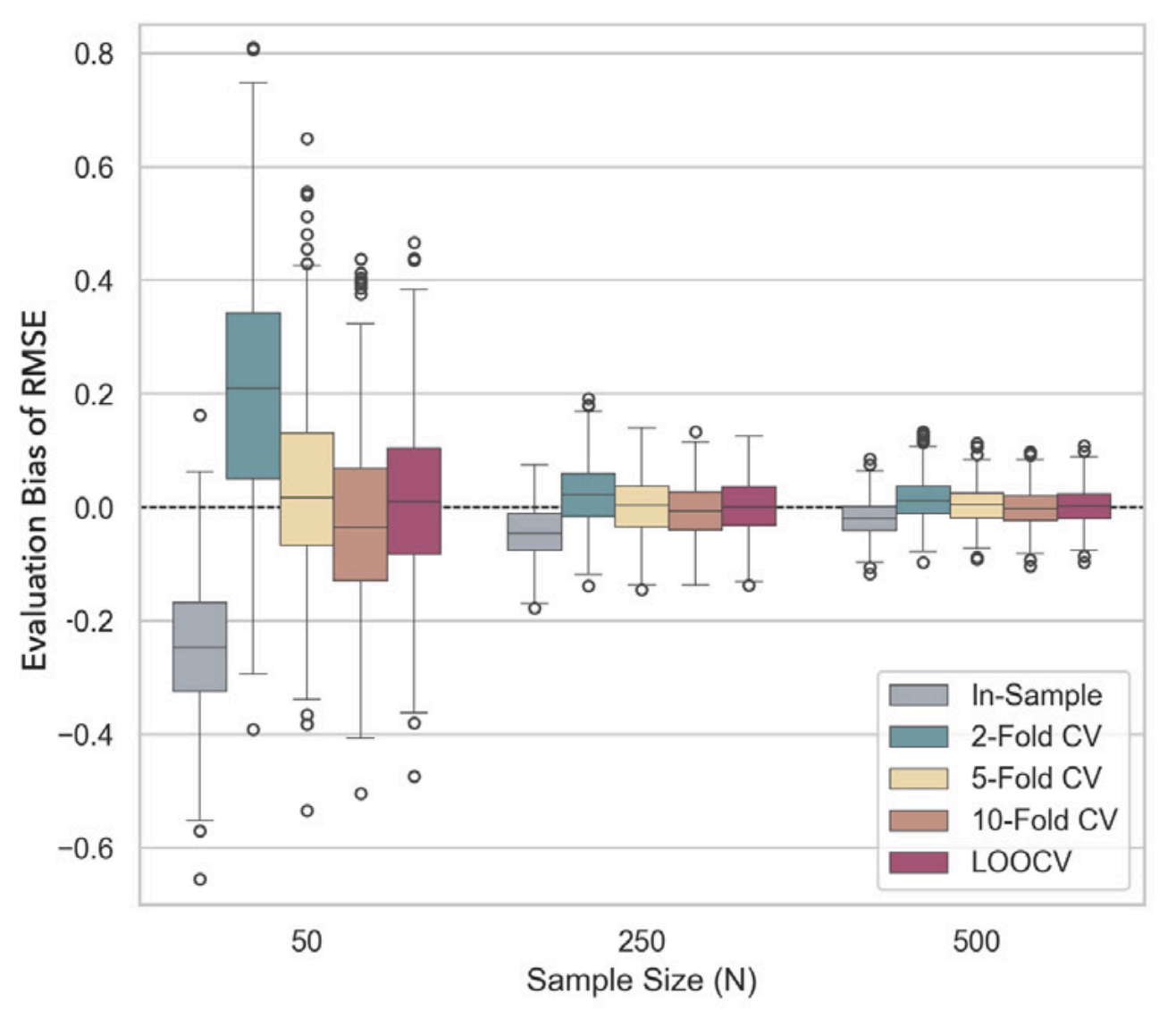
Common Pitfalls in Evaluating Model Performance and Strategies for Avoidance in Agricultural Studies
This study identifies three critical pitfalls in predictive modeling, including improper cross-validation estimators, data leakage during model selection, and neglecting experimental block effects. These issues significantly compromise the reliability of model evaluations in agricultural research. Furthermore, it provides a comprehensive analysis of how various performance metrics behave under different data distributions, offering guidelines for selecting appropriate indicators for both regression (addressing bias and variance) and classification (addressing class imbalance) tasks
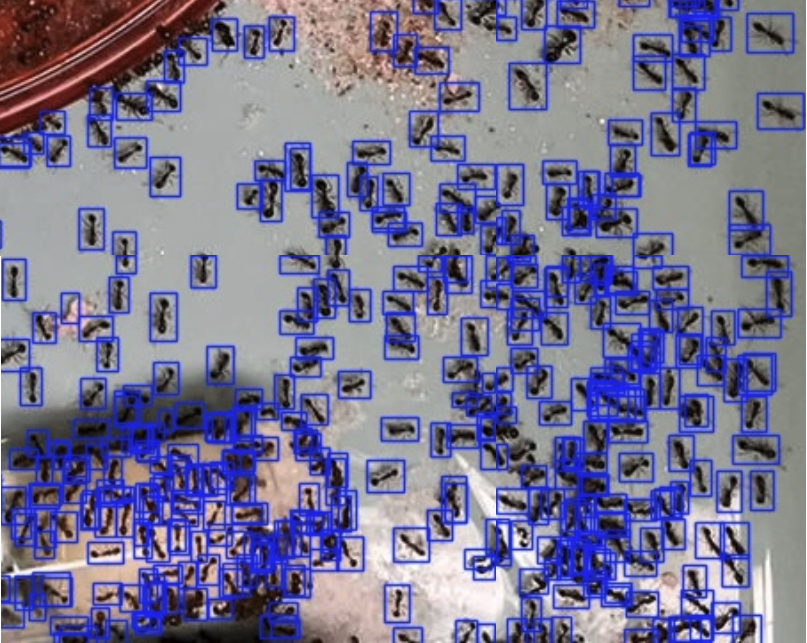
An Automated Approach for Counting Ants in Densely Populated Images and Gaining Insight Into Ant Foraging Behavior
This study presents a hardware-agnostic computer vision workflow that integrates deep learning models with Slicing-Aided Hyper Inference (SAHI) to automate the detection of small, densely packed ants across diverse laboratory environments. By systematically optimizing image slicing parameters, the system overcomes the limitations of standard detectors to achieve high accuracy in scenes containing over a thousand individuals, enabling scalable analysis of foraging behaviors in small insect populations like ants.


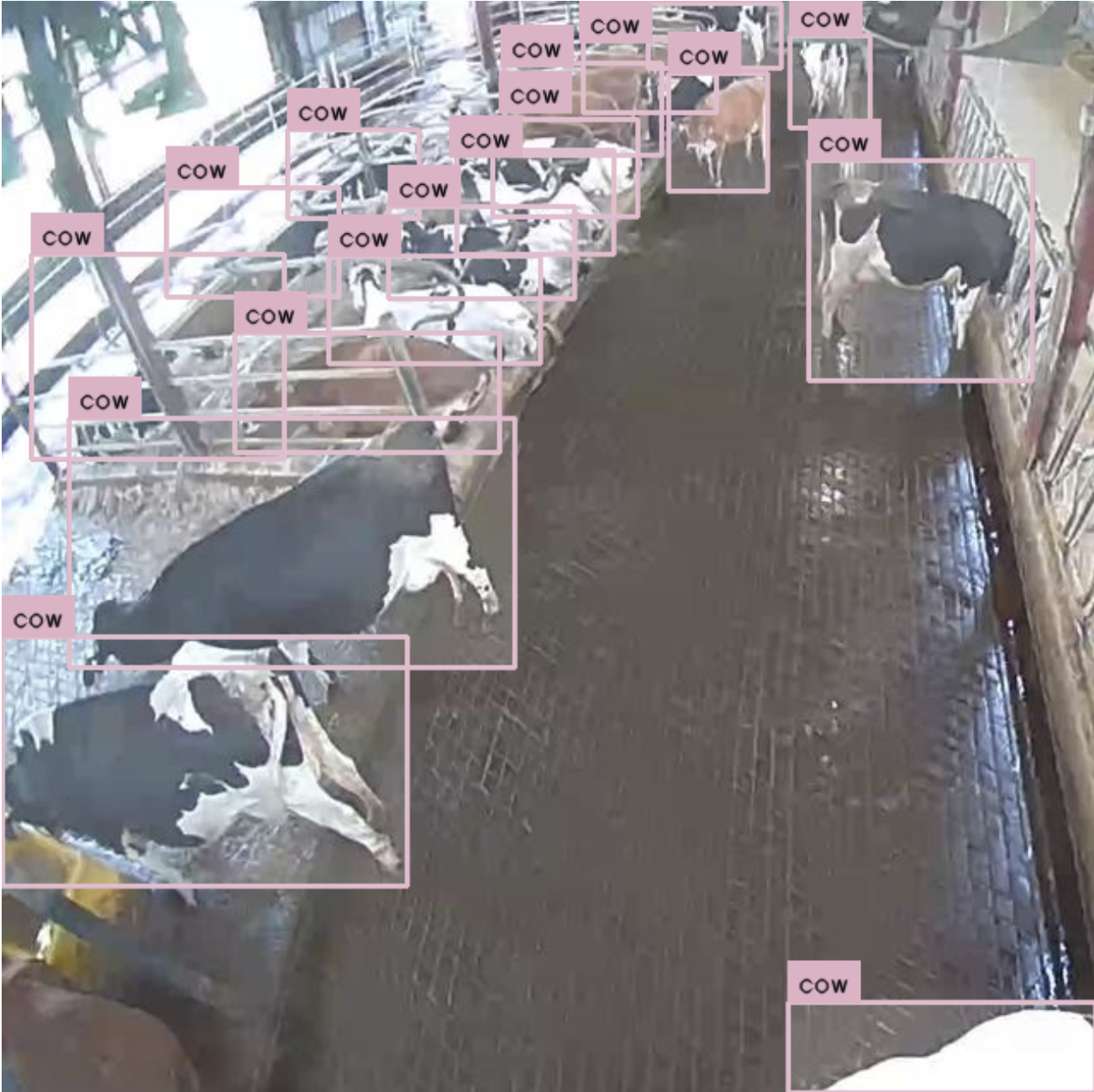
Evaluating Model Generalization for Cow Detection in Free-stall Barn Settings: Insights From the Cow Localization (colo) Dataset
This study evaluates the generalization capabilities of object detection models for localizing cows in free-stall barns, utilizing the COws LOcalization (COLO) dataset to assess performance across varying camera angles and lighting conditions. The findings challenge common assumptions by demonstrating that higher model complexity and task-specific transfer learning do not always yield superior results, providing practical guidelines for deploying computer vision in precision livestock farming.
An Independent Validation Reveals the Potential to Predict Hagberg–perten Falling Number Using Spectrometers
This study presents the first cross-farm and cross-spectral instrument evaluation of a spectroscopy model for predicting Hagberg–Perten falling number (HFN) in wheat, utilizing a dataset spanning multiple locations and years to ensure robustness across different environments. By testing on independent samples collected with different spectral instruments, the research demonstrates a correlation accuracy of 0.72 and highlights the potential for using reduced spectral bands for cost-effective screening

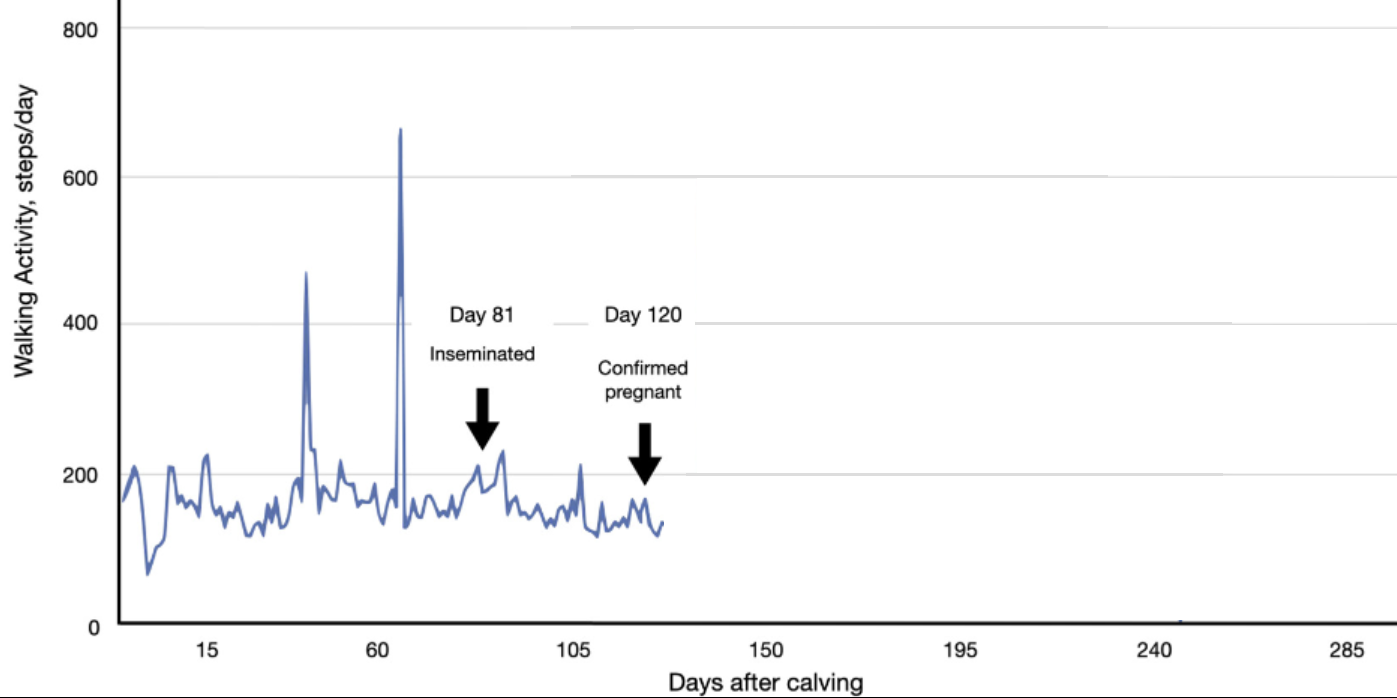
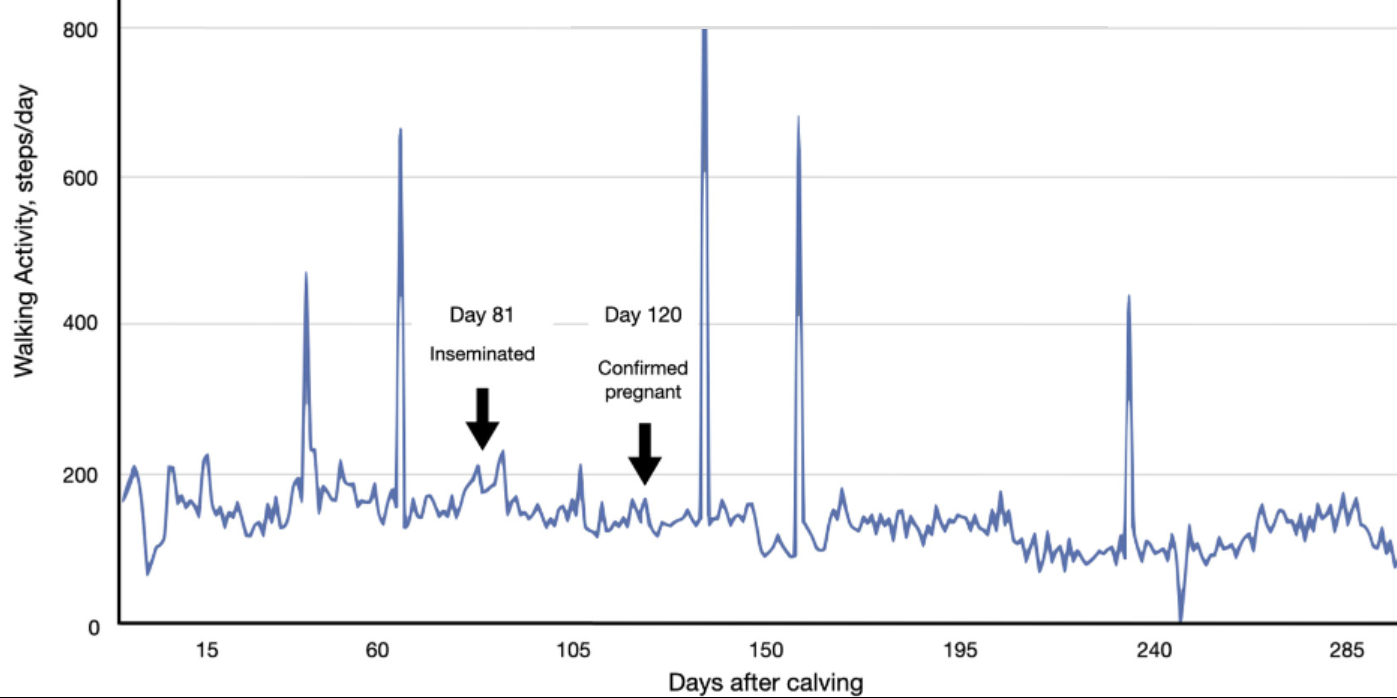
Evaluation of Walking Activity Data During Pregnancy as an Indicator of Pregnancy Loss in Dairy Cattle
This study evaluates whether sudden increases in walking activity (activity peaks) detected by pedometers in pregnant dairy cows are indicative of pregnancy loss,. Analyzing data from 537 pregnancies, the authors determined that activity peaks frequently occur in pregnant cows and should not be misinterpreted as false estrous alerts or signs of abortion.
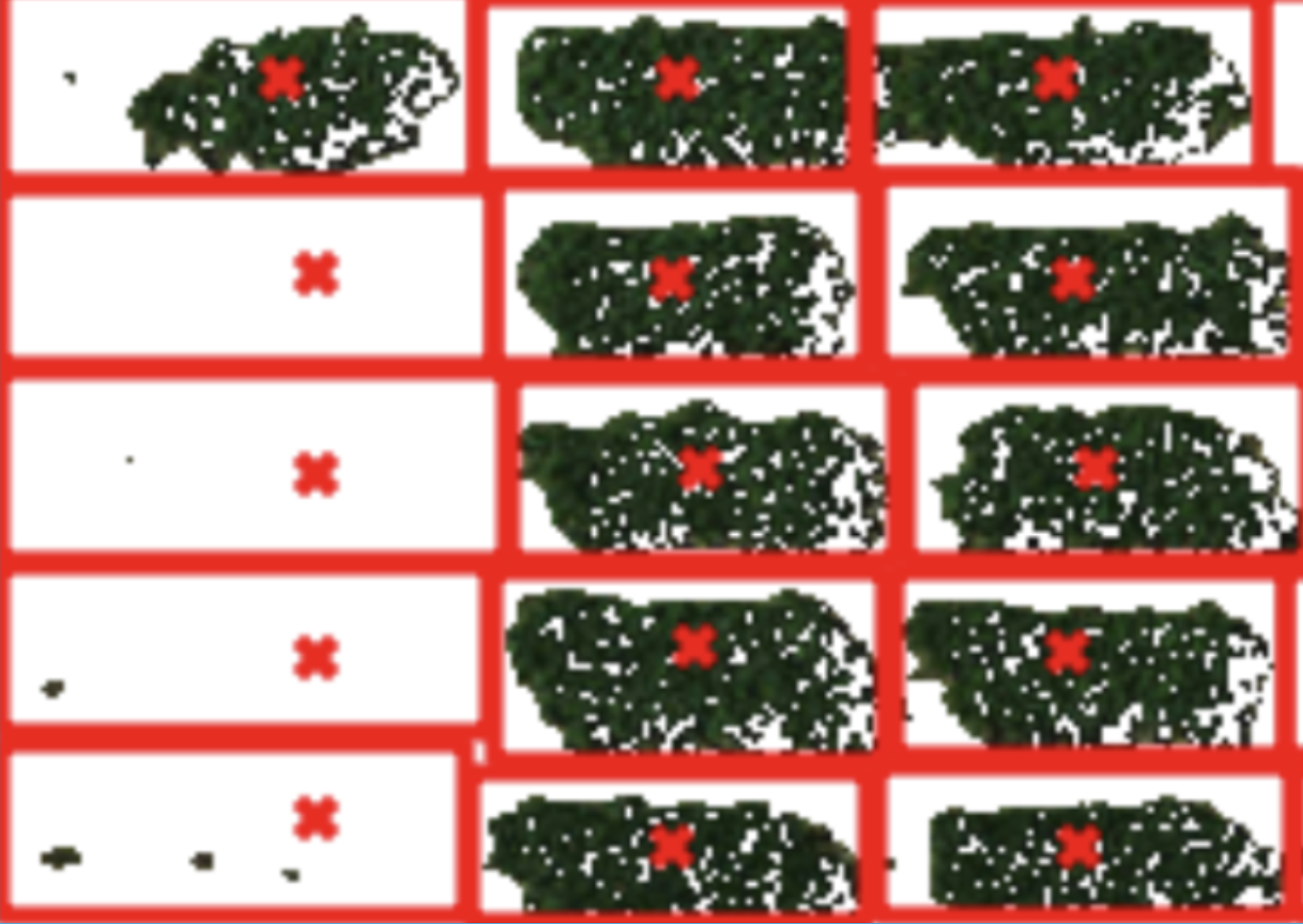
Vtag: a Semi-supervised Pipeline for Tracking Pig Activity With a Single Top-view Camera
VTag is a semi-supervised computer vision pipeline that automates the tracking of group-housed pigs using a single top-view RGB camera, eliminating the need for labor-intensive, pre-labeled training datasets. By employing lightweight algorithms like Sparse Optical Flow, the system achieves high-precision tracking (average error of 17.99 cm) with minimal human supervision, offering a scalable solution for precision livestock farming.
Xsim Version 2: Simulation of Modern Breeding Programs
XSim Version 2 is an efficient, open-source simulation tool implemented in the modern Julia programming language, designed to bridge the gap between theoretical quantitative genetics and practical breeding experiments. By utilizing a 'drop-down' strategy to simulate descendants at sequence-level resolution, XSimV2 offers a user-friendly interface to model complex mating schemes and integrate state-of-the-art statistical models for genetic evaluation.
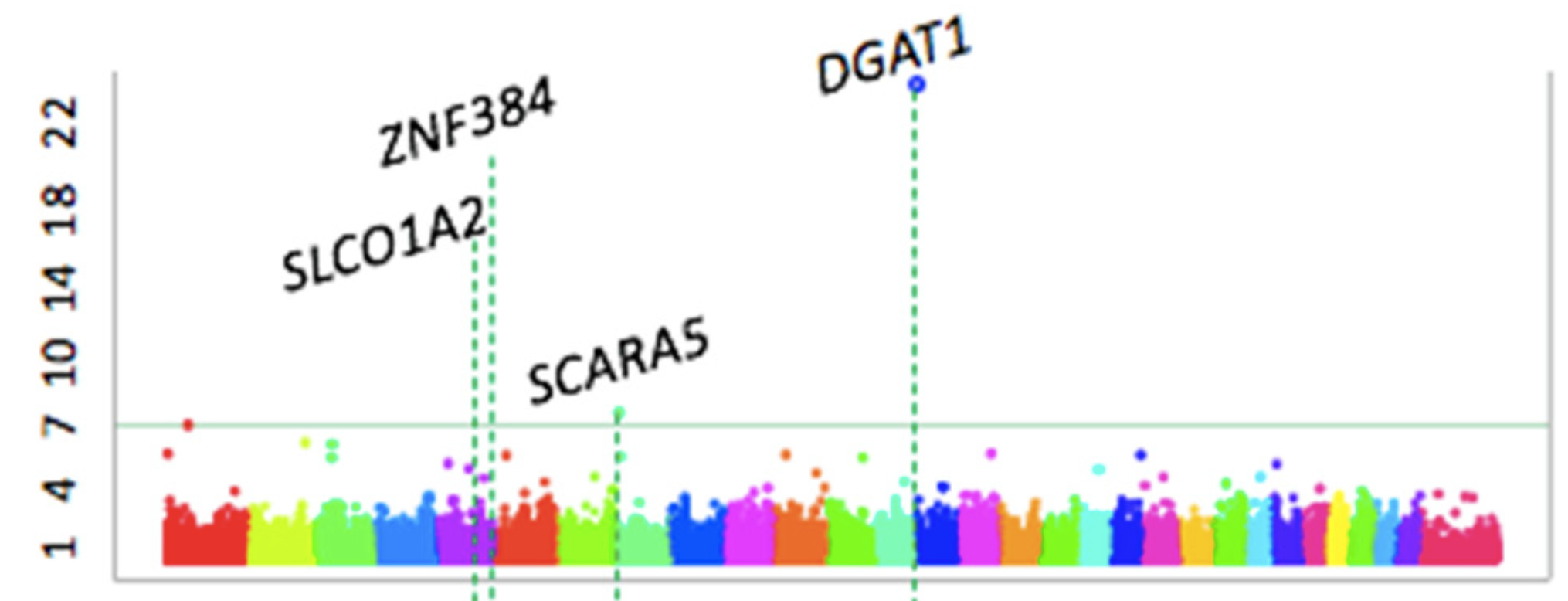
Gwas-based Identification of New Loci for Milk Yield, Fat, and Protein in Holstein Cattle
This study performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) on 1,220 Holstein cows in China to identify genetic variants associated with five milk production and quality traits (milk yield, fat yield, protein yield, fat percentage, and protein percentage). Using the Illumina BovineSNP150 BeadChip and the FarmCPU model to control for population stratification, the researchers identified ten significant SNPs associated with milk fat and protein traits, discovering both known (e.g., DGAT1) and novel candidate genes.
Grid: a Python Package for Field Plot Phenotyping Using Aerial Images
GRID is an open-source Python software designed to advance high-throughput phenotyping by automating the extraction of plot-level data from aerial orthomosaics, effectively bridging the gap between raw imagery and agronomic analysis. By employing K-means clustering and intelligent agent algorithms, the package segments field plots to extract vegetation indices and morphological metrics, allowing users to supervise and refine the process through a user-friendly interface without the need for manual boundary drawing.


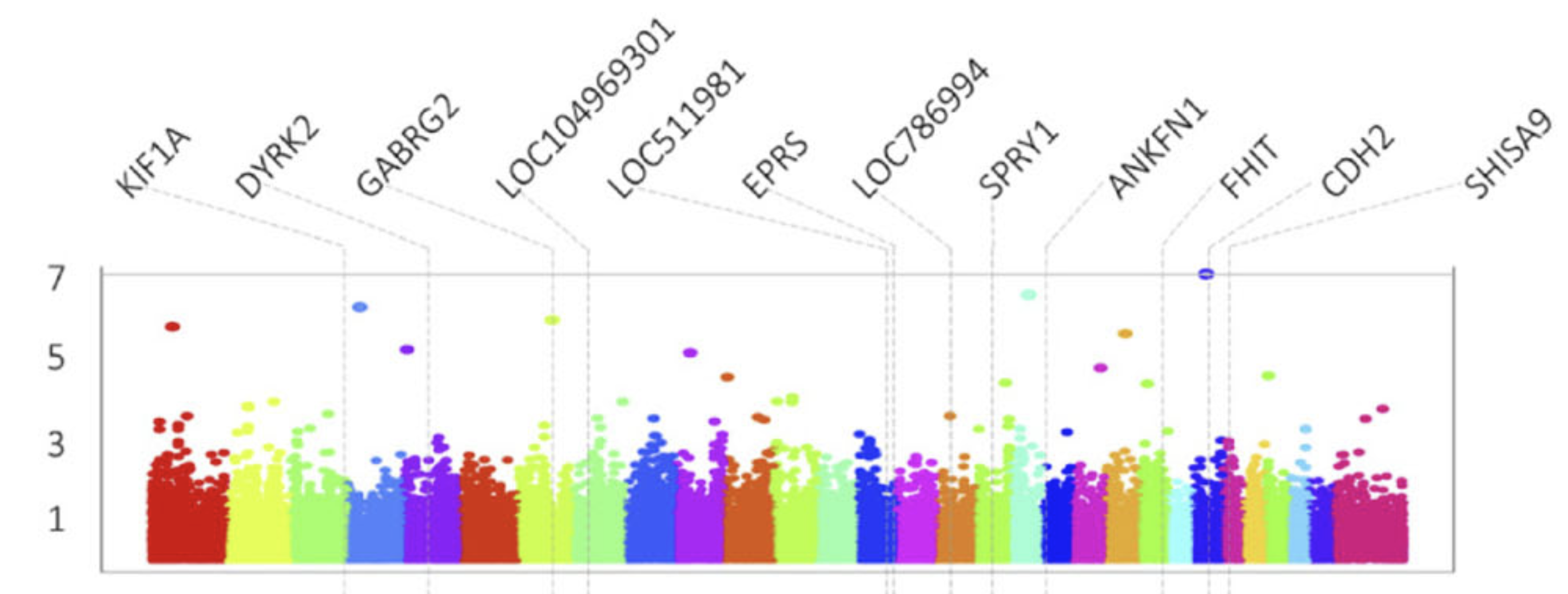
Genome-wide Association Study of Milk and Reproductive Traits in Dual-purpose Xinjiang Brown Cattle
This research represents the first high-density GWAS conducted on Xinjiang Brown cattle, a dual-purpose breed raised in northwestern China, analyzing milk production, reproduction, and mastitis resistance traits. By analyzing phenotypes from 2,410 individuals and genotypes from 403 cows using the 150K Bovine BeadChip, the study identified 12 significant SNPs associated with six traits, providing new insights into the genetic architecture of this unique breed.
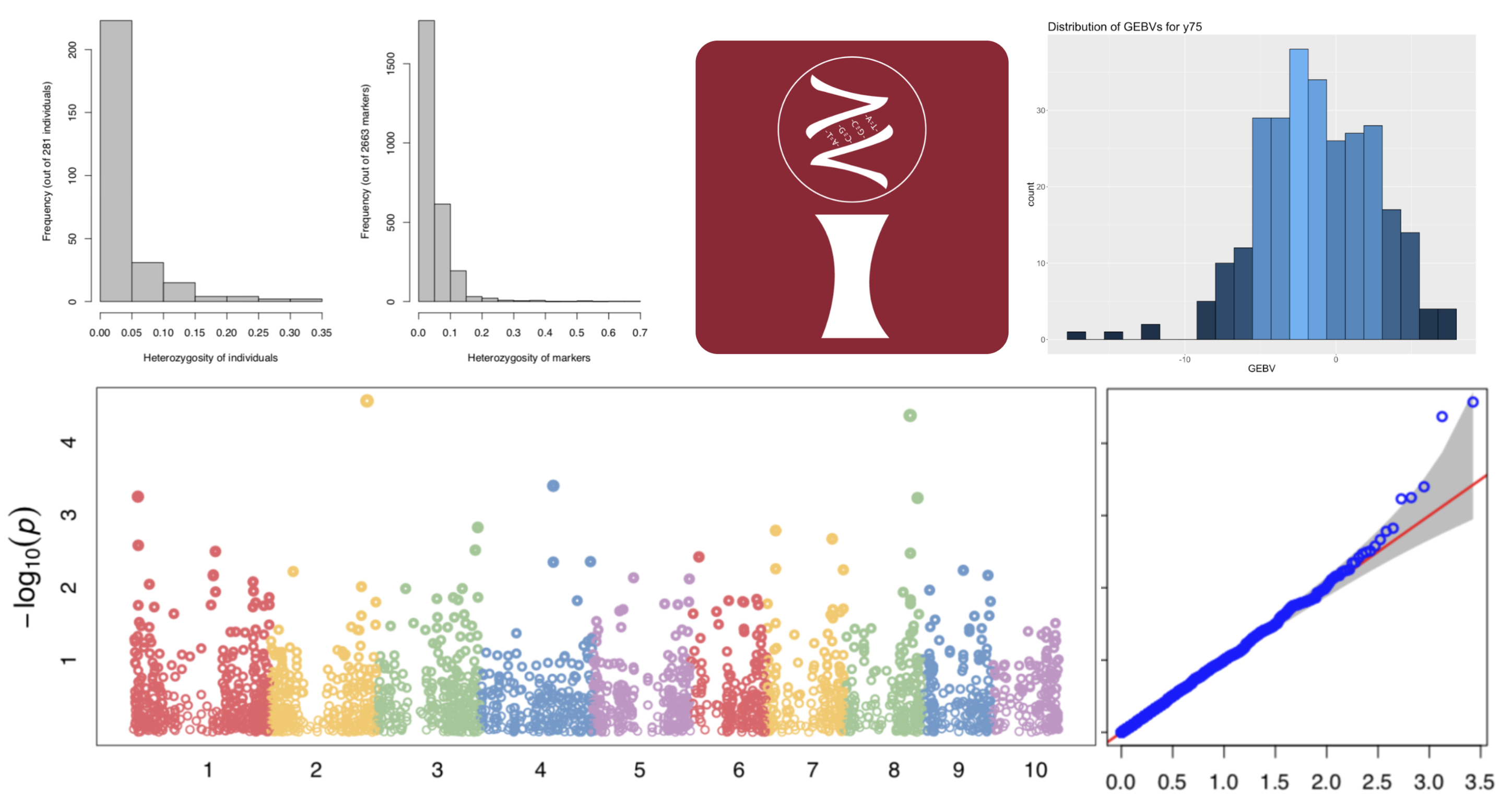
Ipat: Intelligent Prediction and Association Tool for Genomic Research
iPat is a comprehensive software tool that bridges the gap between complex command-line genomic analysis packages and researchers by providing a user-friendly graphical interface for both Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) and Genomic Selection (GS). By wrapping powerful command-line tools like GAPIT and PLINK, iPat allows users to perform sophisticated data analyses and automated format conversions through intuitive drag-and-drop interactions, eliminating the need for programming expertise.