Genome-wide association study of milk and reproductive traits in dual-purpose Xinjiang Brown cattle
Genetic Dissection of a Dual-Purpose Breed
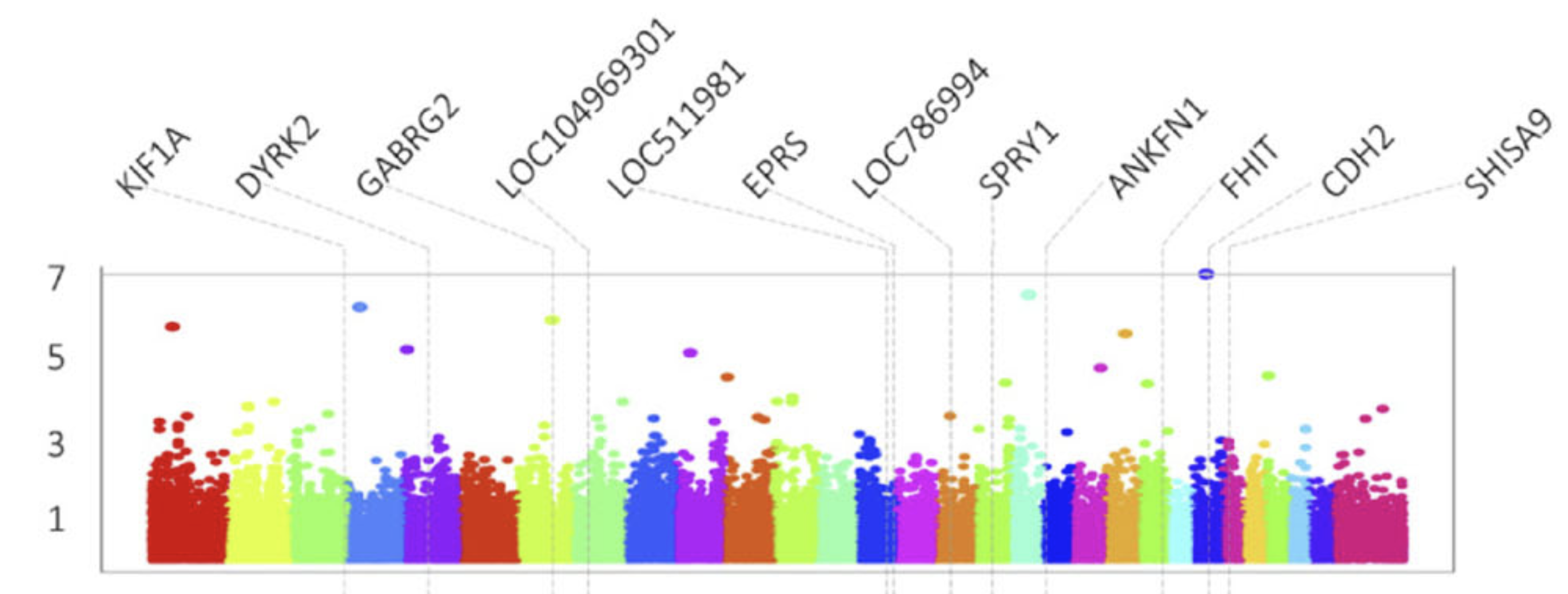
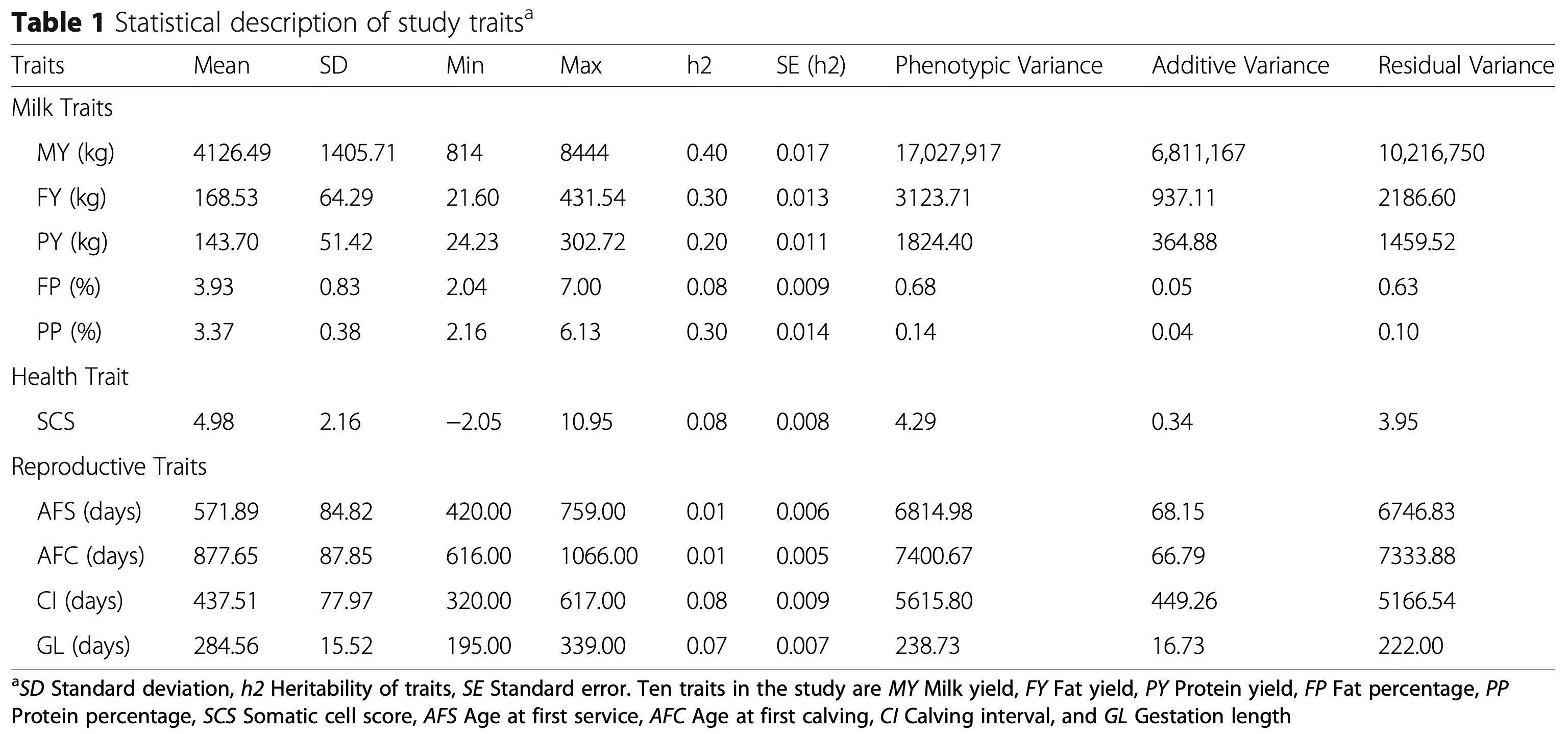
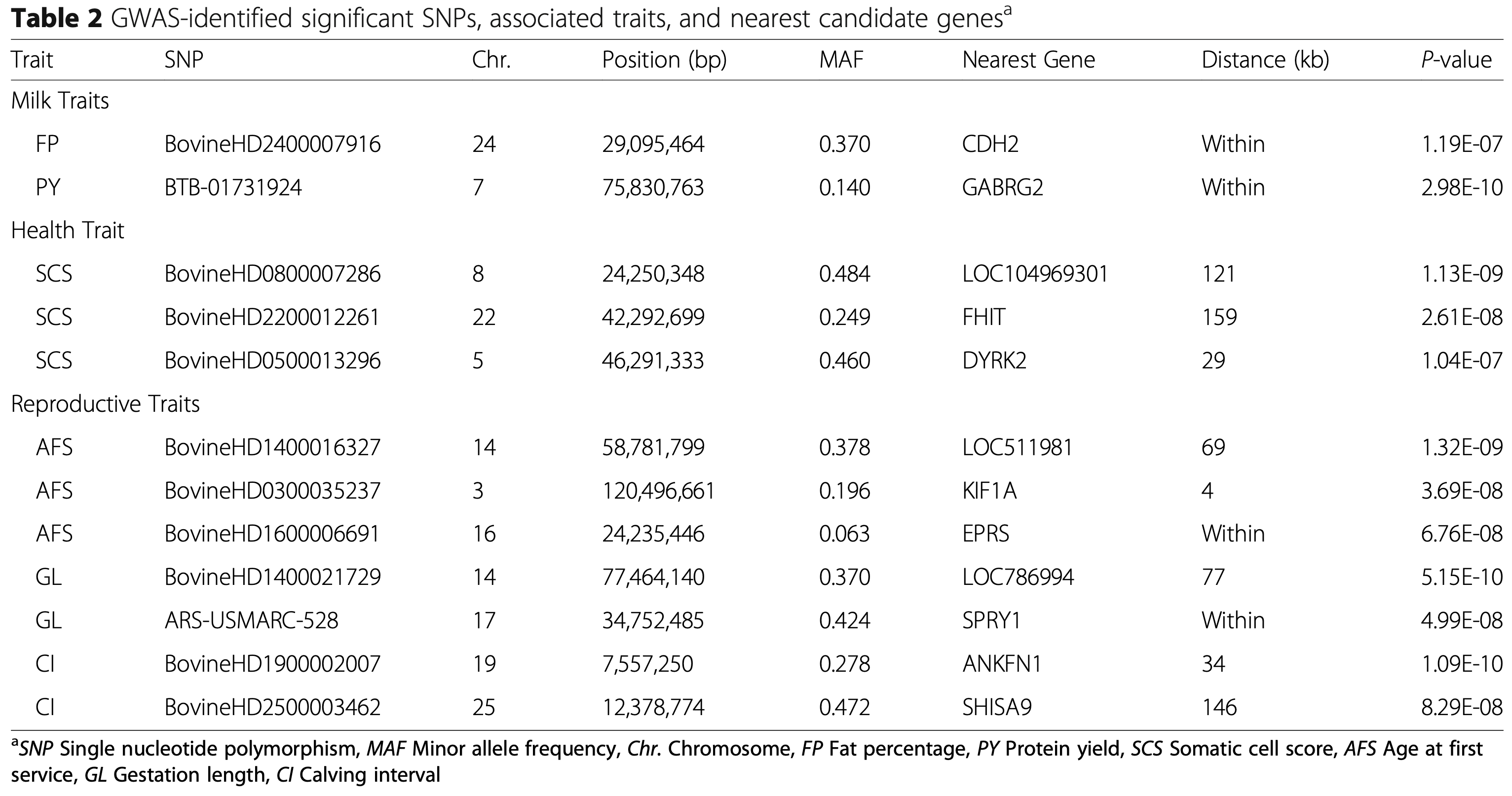
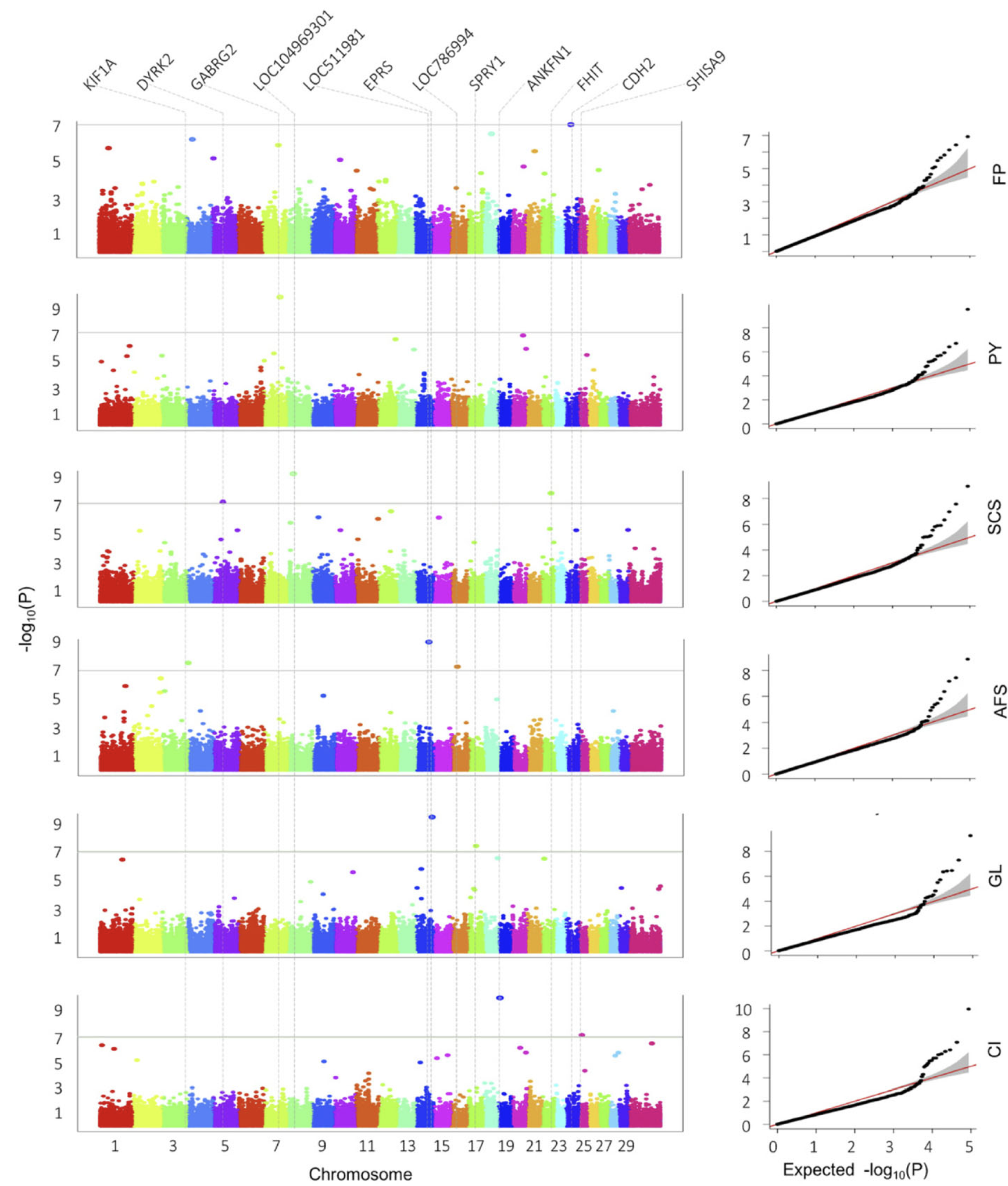
This research focuses on a breed adapted to extreme weather, filling a gap in genomic research which typically focuses on single-purpose dairy or beef cattle. The analysis successfully identified 12 significant markers associated with six of the ten studied traits, including milk fat percentage, protein yield, somatic cell score (health), age at first service, gestation length, and calving interval.
Pleiotropy in Reproductive Traits
The study highlights a significant pleiotropic SNP (BovineHD1600006691) on chromosome 16 that was associated with both age at first service (AFS) and age at first calving (AFC). This specific marker overlaps with a previously reported QTL region associated with calving ease, suggesting that this genomic region plays a critical, multi-faceted role in the reproductive performance of the cattle.
Identification of Functional Candidate Genes
Analysis of the genomic regions surrounding significant SNPs revealed several promising candidate genes with biological functions relevant to the traits. For example, the CDH2 gene on chromosome 24, known to participate in adipogenesis, was linked to milk fat percentage, while the GABRG2 gene on chromosome 7 was associated with milk protein yield, offering potential targets for marker-assisted selection.
